How To Make Excel Calculate In Degrees
This tutorial will demonstrate how to create a normal distribution bell curve in all versions of Excel: 2007, 2010, 2013, 2016, and 2019.
Bell Curve – Free Template Download
Download our free Bell Curve Template for Excel.
Download Now
In statistics, a bong curve (as well known equally a standard normal distribution or Gaussian curve) is a symmetrical graph that illustrates the tendency of data to cluster around a center value, or mean, in a given dataset.
The y-axis represents the relative probability of a given value occurring in the dataset while the x-centrality plots the values themselves on the chart to create a bell-shaped curve, hence the proper noun.
The graph helps us analyze whether a detail value is office of the expected variation or is statistically significant and, therefore, has to be examined more than closely.
Since Excel doesn't have any built-in solutions to offer, you will accept to plot it yourself. That's why we developed the Chart Creator Add together-in, a tool that allows you to build advanced Excel charts in just a few clicks.
In this pace-by-step tutorial, y'all will acquire how to create a normal distribution bell curve in Excel from the ground up:
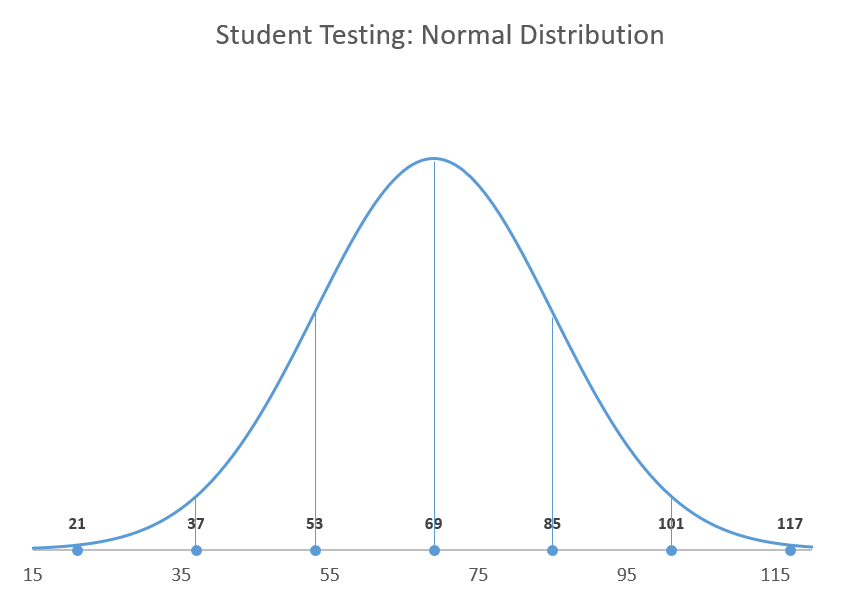
To plot a Gaussian curve, you need to know two things:
- The mean (likewise known as the standard measurement). This determines the centre of the bend—which, in plow, characterizes the position of the curve.
- The standard deviation (SD) of the measurements. This defines the spread of your information in the normal distribution—or in plain English, how broad the curve should exist. For case, in the bell curve shown to a higher place, one standard difference of the mean represents the range betwixt exam scores of 53 and 85.
The lower the SD, the taller the curve and the less your information volition exist spread out, and vice versa.
It's worth mentioning the 68-95-99.7 rule that can be applied to any normal distribution curve, meaning roughly 68% of your data is going to be placed within one SD away from the hateful, 95% within 2 SD, and 99.7% within three SD.
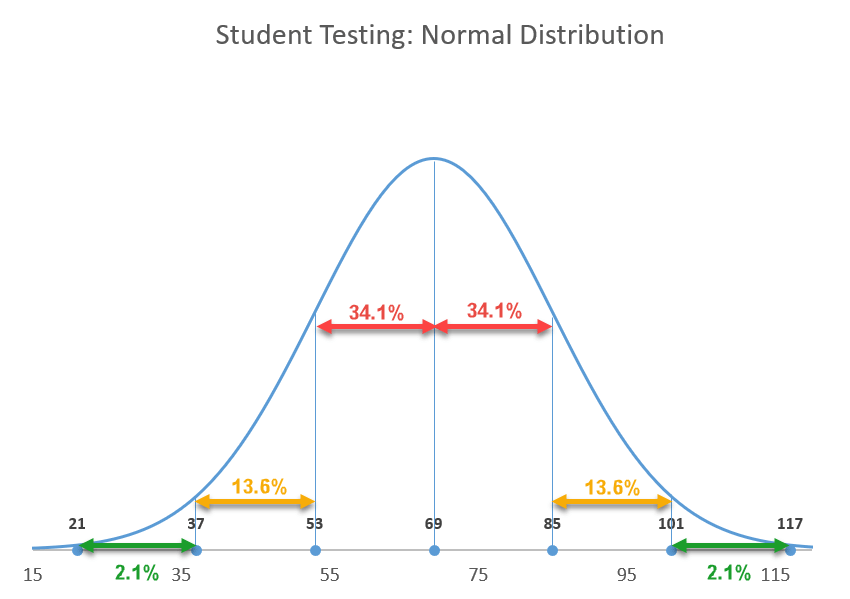
Now that you know the essentials, permit's move from theory to exercise.
Getting Started
For illustration purposes, let's presume you have the test scores of 200 students and want to class them "on a curve," meaning the students' grades will be based on their relative operation to the rest of the form:
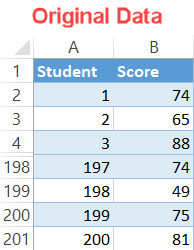
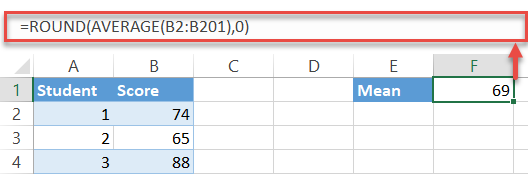
Pace #1: Observe the hateful.
Typically, y'all are given the mean and SD values from the start, but if that'south not the case, you tin can easily compute these values in just a few unproblematic steps. Let'south tackle the mean commencement.
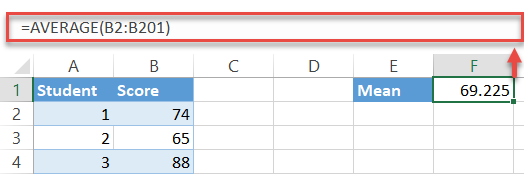
Since the mean indicates the average value of a sample or population of data, you tin can detect your standard measurement using the AVERAGE office.
Type the following formula into whatever empty jail cell (F1 in this example) next to your bodily data (columns A and B) to calculate the average of the test scores in the dataset:
A quick notation: more often than not, you may need to round up the formula output. To practice that, simply wrap it in the ROUND part as follows:
| =ROUND ( AVERAGE ( B2 : B201 ) , 0 ) |
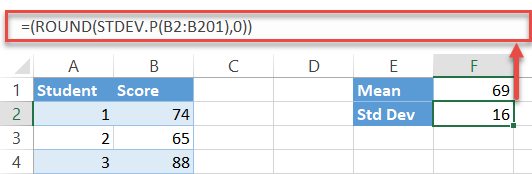
Step #2: Notice the standard departure.
I down, 1 to become. Fortunately, Excel has a special function to practice all the muddied piece of work of finding the standard deviation for you:
Over again, the formula picks all the values from the specified cell range (B2:B201) and computes its standard deviation—just don't forget to round up the output besides.
| =ROUND ( STDEV . P ( B2 : B201 ) , 0 ) |
Stride #iii: Gear up the 10-axis values for the curve.
Basically, the chart constitutes a massive number of intervals (think of them as steps) joined together with a line to create a polish bend.
In our case, the x-axis values will exist used to illustrate a particular test score while the y-axis values volition tell u.s.a. the probability of a educatee getting that score on the exam.
Technically, you tin can include as many intervals equally yous want—you can effortlessly erase the redundant data afterward by modifying the horizontal centrality calibration. Just make sure yous pick a range that volition comprise the three standard deviations.
Allow'south start a count at one (equally there is no way a student can go a negative exam score) and become all the fashion upwards to 150—it doesn't really thing whether it's 150 or 1500—to fix another helper table.
- Pick any empty jail cell below the chart information (such as E4) and type "one," the value that defines the first interval.
- Navigate to the Abode tab.
- In the Editing group, choose "Fill."
- Nether "Series in," select "Cavalcade."
- For "Step value," type "1." This value determines the increments that will be automatically added upwards until Excel reaches the last interval.
- For "Stop value," type "150," the value that stands for the last interval, and click "OK."
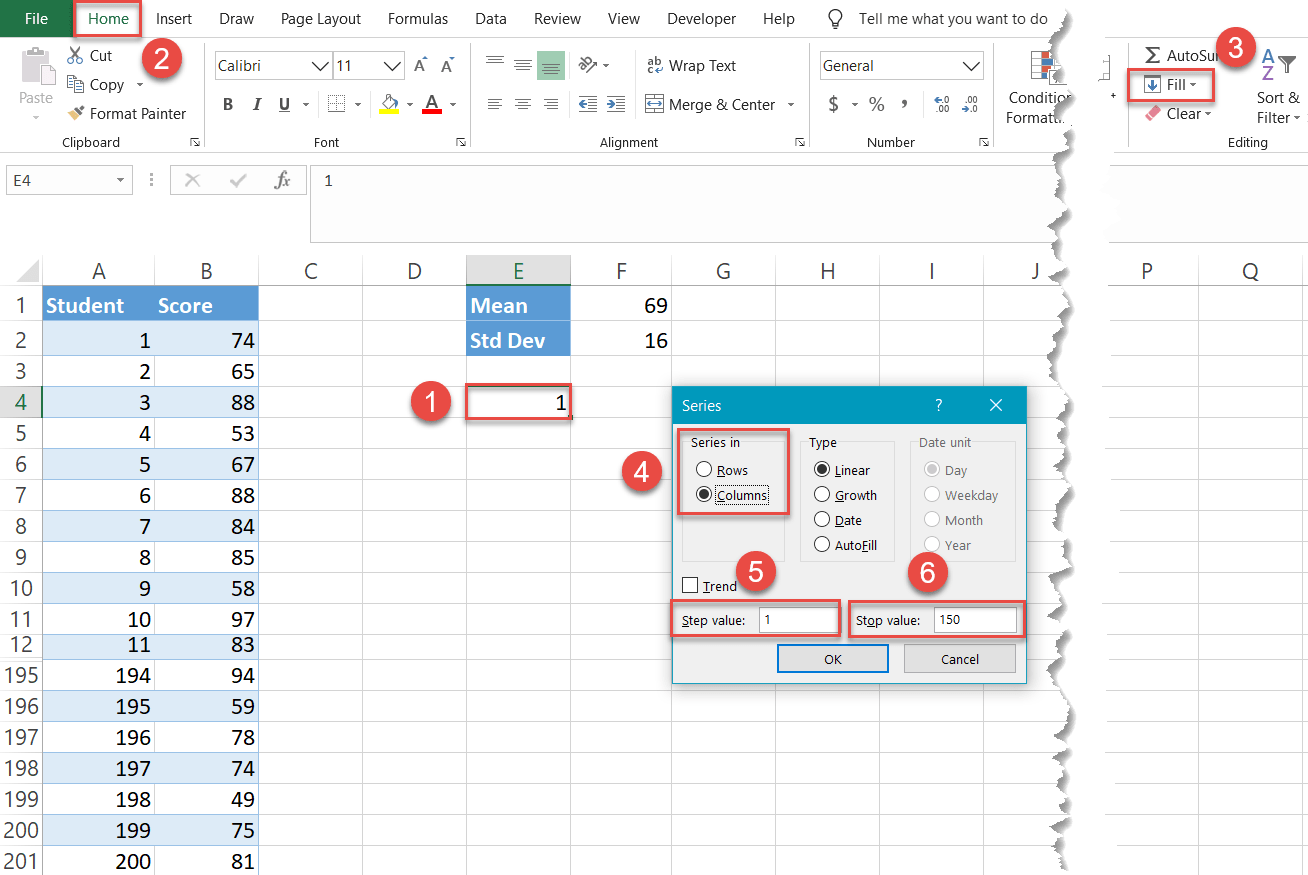
Miraculously, 149 cells in column East (E5:E153) accept been filled with the values going from ii to 150.
NOTE: Exercise not hide the original data cells as shown on the screenshots. Otherwise, the technique will not piece of work.
Step #four: Compute the normal distribution values for every x-axis value.
Now, find the normal distribution values—the probability of a student getting a certain test score represented by a detail 10-centrality value—for each of the intervals. Fortunately for you, Excel has the workhorse to do all these calculations for you: the NORM.DIST function.
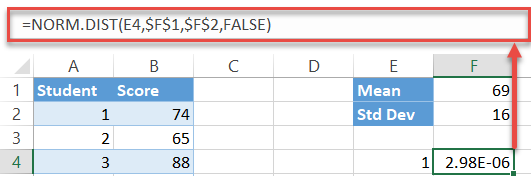
Type the following formula into the jail cell to the correct (F4) of your first interval (E4):
| =NORM . DIST ( E4 , $ F $ i , $ F $ 2 , Fake ) |
Here is the decoded version to help you suit appropriately:
| =NORM . DIST ( [ the first interval ] , [ the mean ( absolute reference ) ] , [ the standard divergence ( absolute reference ) , Faux ) |
You lot lock the mean and SD values so that you can effortlessly execute the formula for the remaining intervals (E5:E153).
Now, double-click on the make full handle to copy the formula into the remainder of the cells (F5:F153).
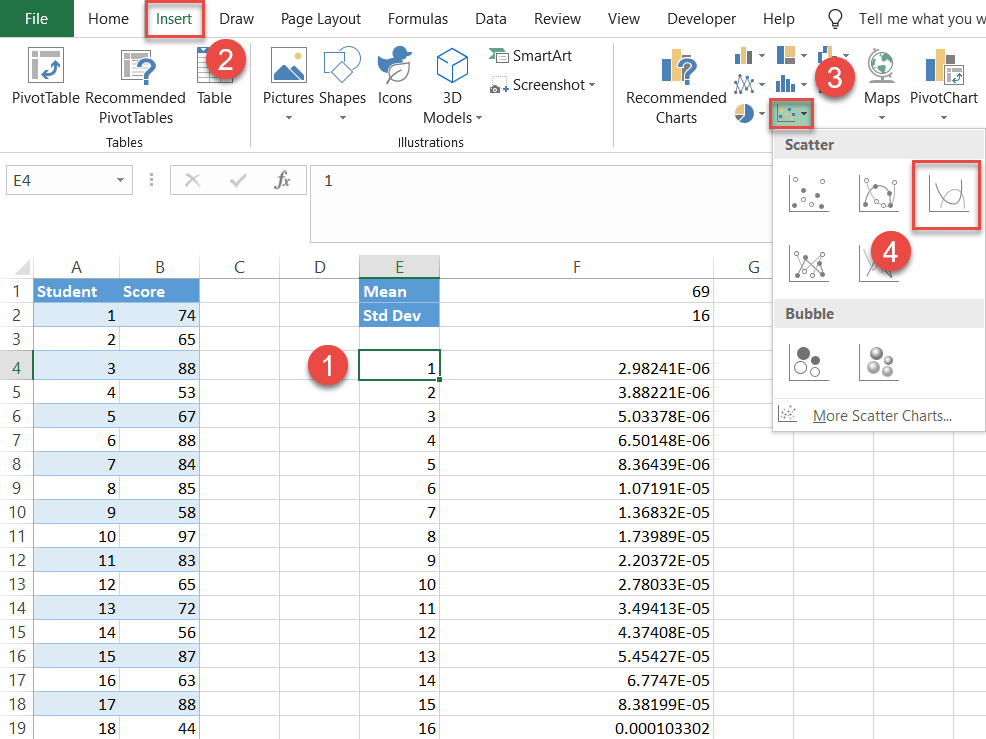
Step #5: Create a scatter plot with smoothen lines.
Finally, the time to build the bell curve has come up:
- Select whatsoever value in the helper tabular array containing the x- and y-axis values (E4:F153).
- Go to the Insert tab.
- Click the "Insert Scatter (Ten, Y) or Bubble Chart" push.
- Cull "Scatter with Smooth Lines."
Step #six: Prepare the label tabular array.
Technically, yous take your bell bend. But information technology would exist hard to read as it lacks whatever data describing it.
Let'southward brand the normal distribution more informative by calculation the labels illustrating all the standard divergence values below and in a higher place the mean (you can also use them for showing the z-scores instead).
For that, set upwardly still another helper table as follows:
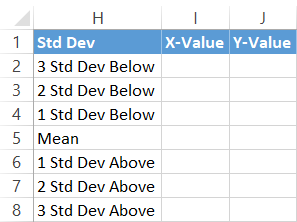
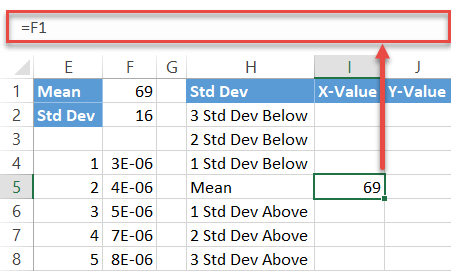
First, copy the Mean value (F1) next to the corresponding cell in column X-Value (I5).
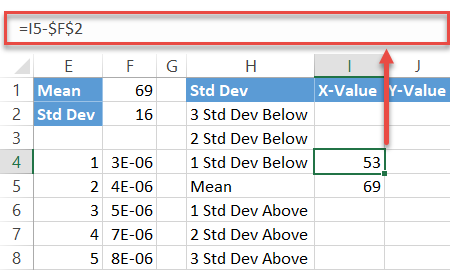
Next, compute the standard deviation values below the hateful by inbound this uncomplicated formula into cell I4:
Simply put, the formula subtracts the sum of the preceding standard deviation values from the mean. Now, drag the fill handle upward to copy the formula into the remaining two cells (I2:I3).
Echo the same process for the standard deviations above the hateful using the mirror formula:
In the same way, execute the formula for the other two cells (I7:I8).
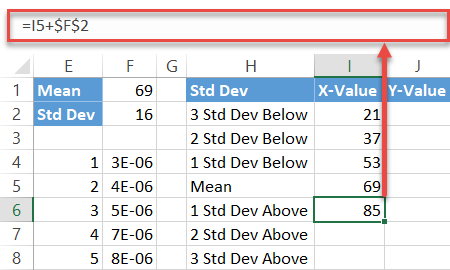
Finally, fill the y-centrality label values (J2:J8) with zeros as you desire the data markers placed on the horizontal centrality.
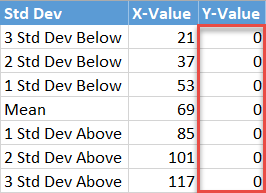
Pace #7: Insert the label data into the nautical chart.
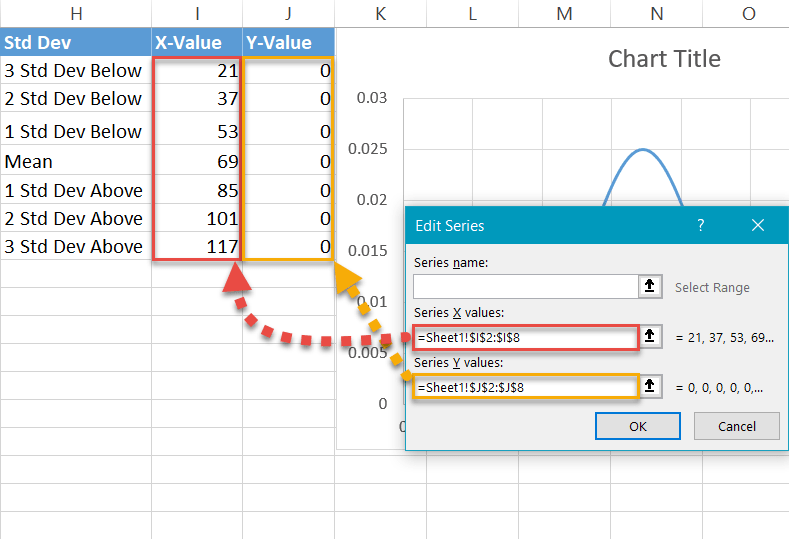
At present, add all the data y'all have prepared. Right-click on the chart plot and choose "Select Data."
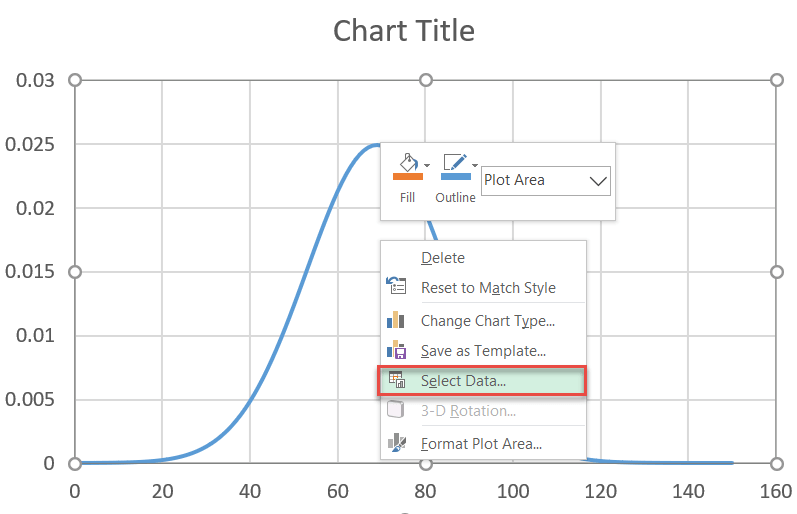
In the dialog box that pops up, select "Add."
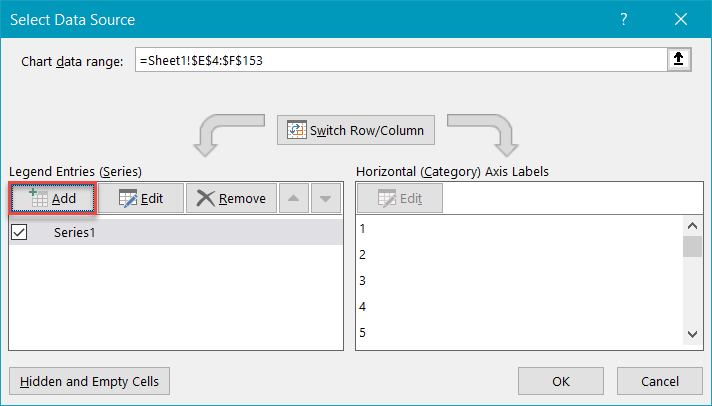
Highlight the respective cells ranges from the helper table—I2:I8 for "Serial X values" and J2:J8 for "Serial Y values"—and click "OK."
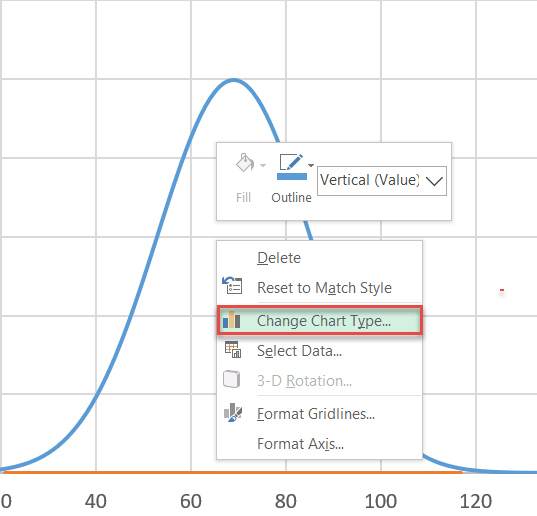
Stride #8: Change the chart type of the label series.
Our next pace is to alter the chart blazon of the newly-added series to brand the information markers appear as dots. To do that, right-click on the nautical chart plot and select "Change Chart Type."
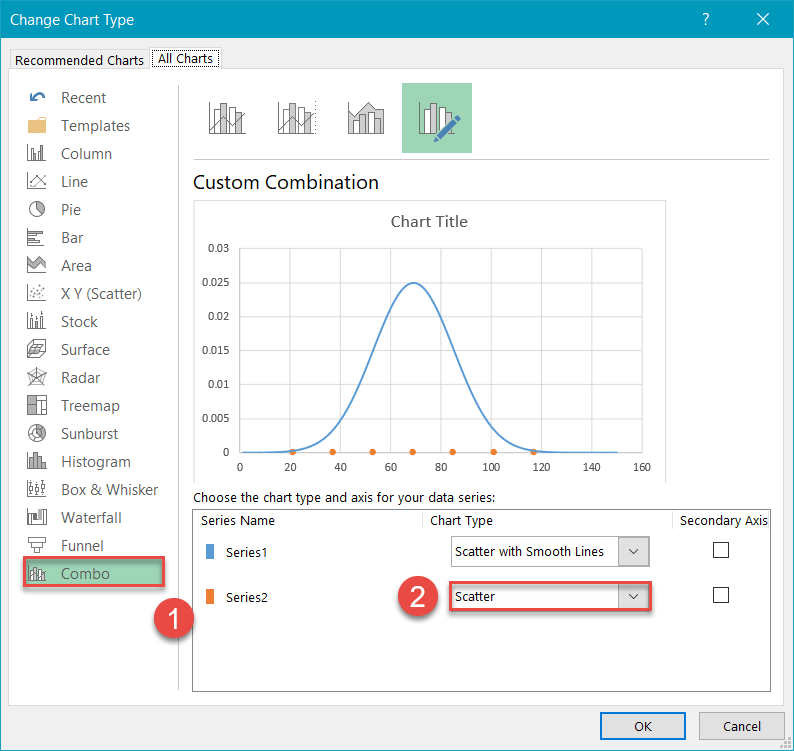
Adjacent, pattern a combo chart:
- Navigate to the Combo tab.
- For Serial "Series2," change "Nautical chart Type" to "Scatter."
- Annotation: Make sure "Series1" remains as "Besprinkle with Smoothen Lines." Sometimes Excel will modify it when you make a Combo Also brand sure "Series1" is non pushed to the Secondary Centrality—the bank check box side by side to the nautical chart type should not exist marked.
- Click "OK."
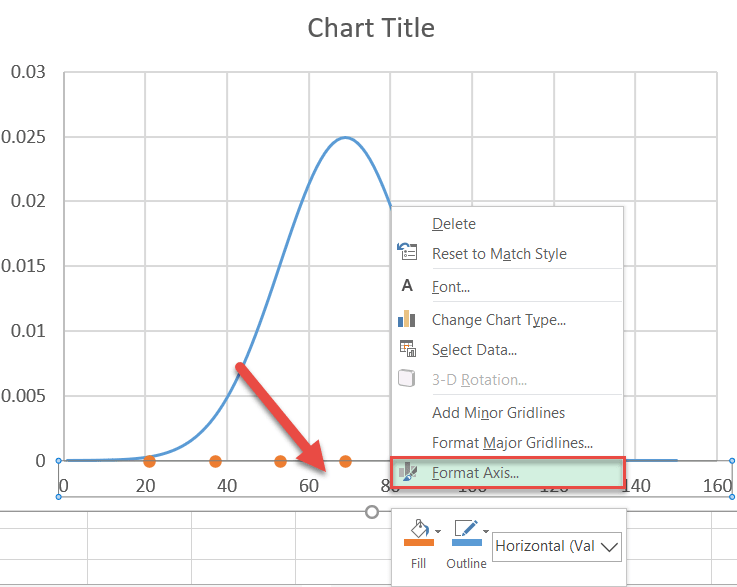
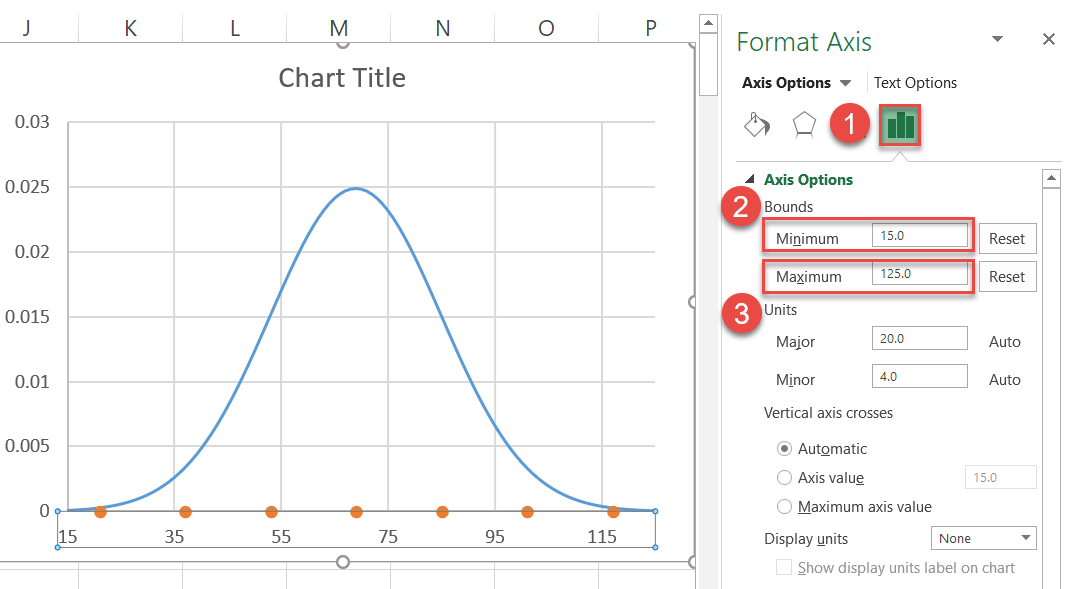
Stride #9: Modify the horizontal centrality scale.
Heart the nautical chart on the bell curve by adjusting the horizontal axis scale. Right-click on the horizontal axis and choice "Format Axis" from the menu.
In one case the task pane appears, do the post-obit:
- Go to the Axis Options tab.
- Gear up the Minimum Bounds value to "15."
- Fix the Maximum Bounds value to "125."
You tin tweak the centrality scale range notwithstanding you see fit, but since you lot know the standard deviation ranges, fix the Premises values a bit abroad from each of your third standard deviations to show the "tail" of the curve.
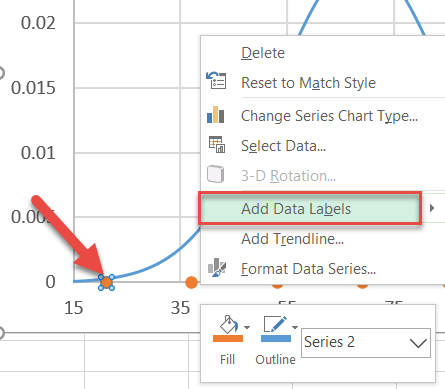
Stride #x: Insert and position the custom information labels.
As y'all smooth up your chart, exist sure to add the custom information labels. First, right-click on whatever dot representing Series "Series2" and select "Add Data Labels."
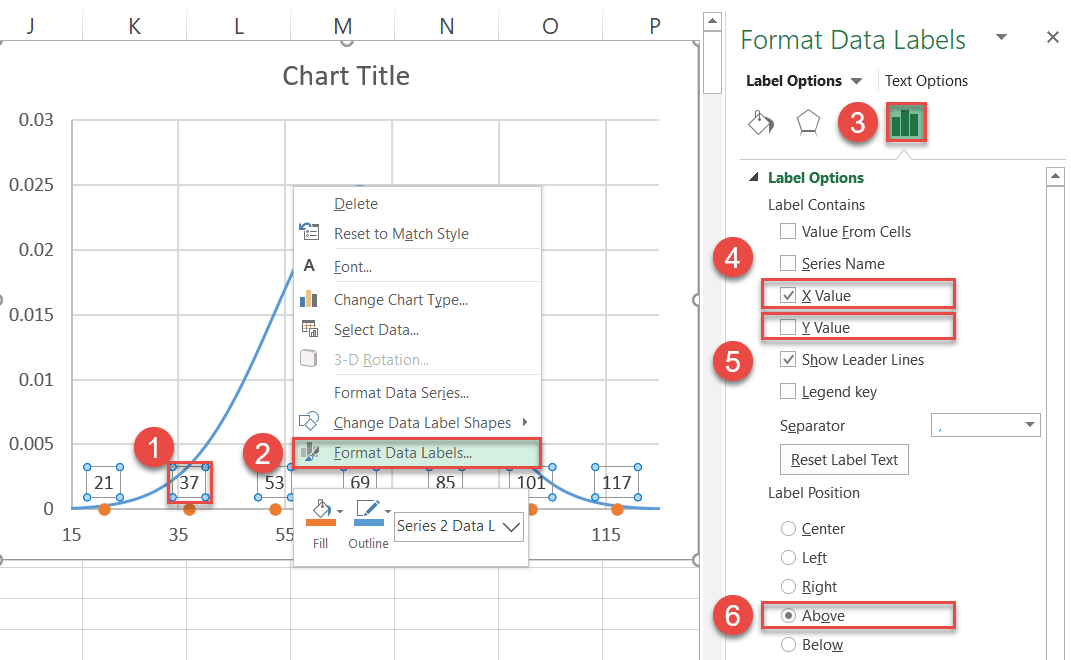
Side by side, replace the default labels with the ones you previously fix up and place them in a higher place the data markers.
- Right-click on any Serial "Series2" data label.
- Select "Format Data Labels."
- In the job pane, switch to the Label Options tab.
- Check the "X Value" box.
- Uncheck the "Y Value" box.
- Nether "Label Position," choose "Above."
Also, you can now remove the gridlines (right-click on them > Delete).
Step #11: Recolor the data markers (optional).
Finally, recolor the dots to assistance them fit into your chart style.
- Right-click on any Series "Series2" data label.
- Click the "Fill" push button.
- Pick your color from the palette that appears.
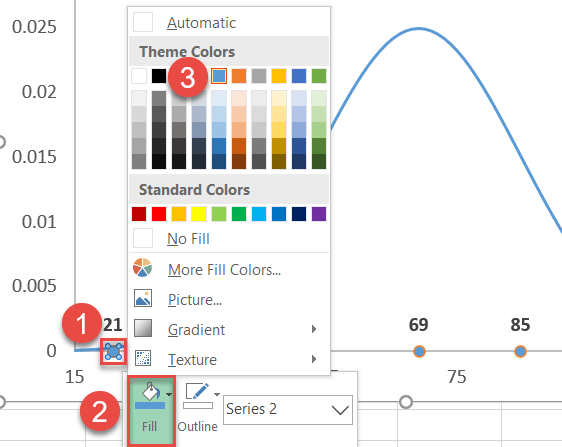
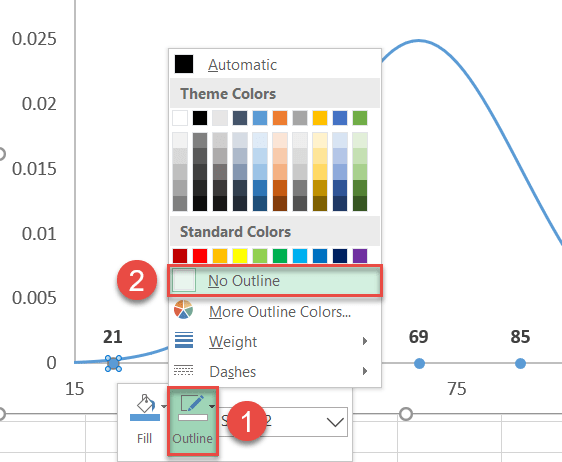
As well, remove the borders effectually the dots:
- Right-click on the same data marker once more and select "Outline."
- Cull "No Outline."
Step #12: Add vertical lines (optional).
As a final aligning, y'all can add vertical lines to the chart to help emphasize the SD values.
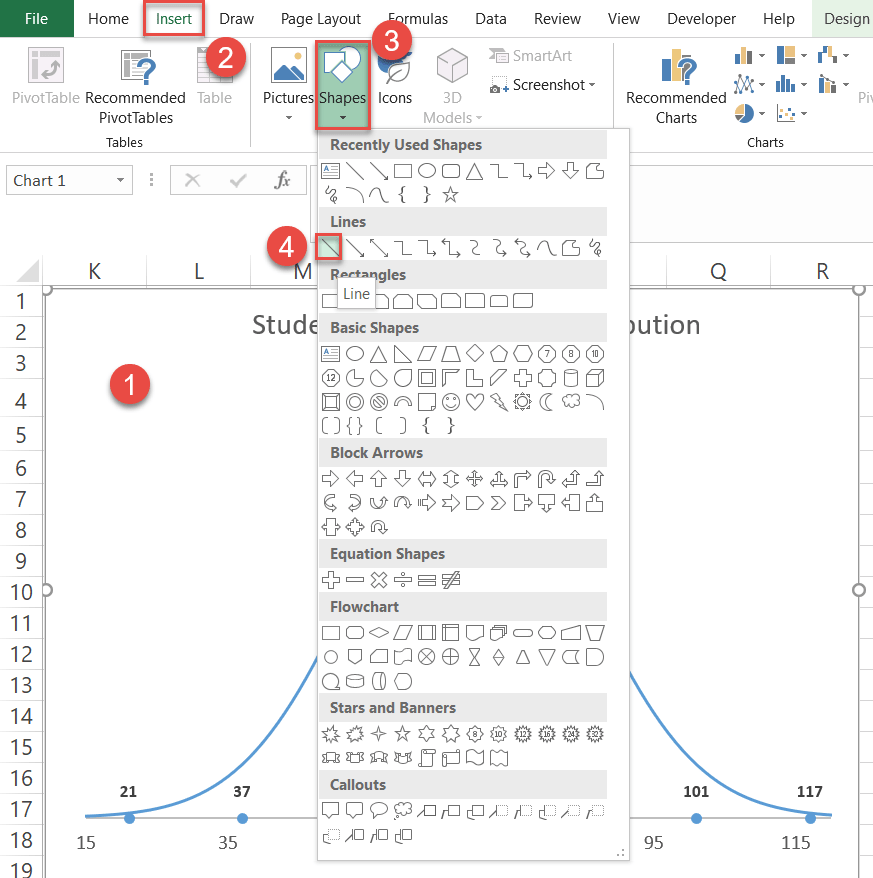
- Select the nautical chart plot (that way, the lines will be inserted directly into the chart).
- Become to the Insert tab.
- Click the "Shapes" button.
- Cull "Line."
Hold down the "SHIFT" primal while dragging the mouse to describe perfectly vertical lines from each dot to where each line meets the bell curve.
Change the chart title, and your improved bell curve is ready—showing your valuable distribution data.

And that's how you do it. Y'all tin now option whatever dataset and create a normal distribution bell curve following these simple steps!
Download Normal Distribution Bell Bend Template
Download our gratuitous Normal Distribution Bell Bend Template for Excel.
Download At present
Source: https://www.automateexcel.com/charts/bell-curve-plot-template/
Posted by: rosswharry.blogspot.com


0 Response to "How To Make Excel Calculate In Degrees"
Post a Comment